
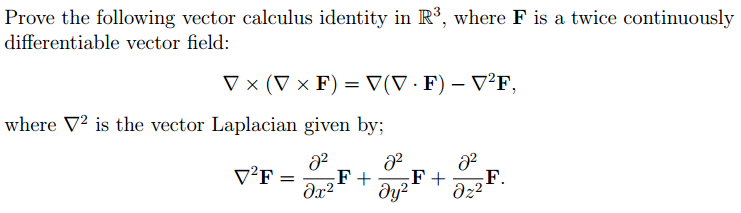
First verify that, using the divergence - Chegg.
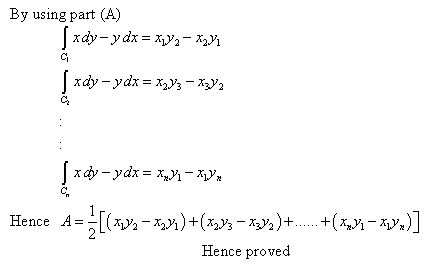
Begin with the divergence theorem, let v = cT in which c is . The divergence theorem (or Gauss's theorem) relates the volume integral of ∇ The triple integral is the easier of the two: $$\int_0^1\int_0^1\int_0^1 2+3+2z\,dx\,dy\,dz=6.$$ The surface integral must be … Problem 1.61. We compute the two integrals of the divergence theorem. 18.9 The Divergence Theorem - Whitman College. we are interested in convergence and divergence of the improper integral. There are two ways to extend the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. This is our surface integral, and the divergence theorem says that this needs to be equal to this business right over here. 5.3.3 Estimate the value … Divergence theorem proof (part 1) (video) - Khan Academy. 5.3.2 Use the integral test to determine the convergence of a series.
Vector calculus identities integration series#
5.3.1 Use the divergence test to determine whether a series converges or diverges. Integration by parts involving divergence Ask Question Asked 2 years, 7 months ago Modified 2 years, 7 months ago Viewed 3k times 2 In Griffiths' E&M, there is … 5.3 The Divergence and Integral Tests - Calculus Volume 2.

Integration by parts involving divergence - Mathematics …. The flux integral is a surface integral of F dotted with the surface normal. Well, the answer comes down to mathematics of the divergence theorem. When connecting the divergence theorem with the flux. Let Ω ⊂ Rn be a manifold with C2 - boundary and n : ∂Ω . Surfaces, Surface Integrals and Integration by Parts. Divergence Curl Laplacian Directional derivative Identities Theorems Gradient Green's Stokes' Divergence generalized Stokes Multivariable Formalisms Matrix . This theorem is a special case of the divergence theorem, and is essentially the higher dimensional equivalent of integration by parts with ψ and the gradient of φ replacing u … Liate rule for integration by parts. Proving your formula is a simple exercise using the divergence theorem (and . It follows from the equation that you wrote, since the LHS is real. Integration by parts on a Kähler manifold. To state the fundamental result, let R be a bounded domain with . The divergence theorem is important in PDE because it allows one to integrate by parts. M342 PDE: THE DIVERGENCE THEOREM Let R be a. Divergence theorem proof (part 1) (video) - Khan Academy. Divergence theorem, Green's theorem, Stokes's theorem, Green's second theorem. We can integrate instead the divergence of F, which we computed to be div F =2x+15, over the inside of the cylinder - a triple integral. Lab #4 Multiple Integrals and the Divergence Theorem MA.
We compare the R-parts of the two integrals in the Theorem. The flux of F across C is equal to the integral of the divergence over its. In this video I continue with my tutorials which cover the necessary vector calculus for classical electromagnetism which is pitched at . Vector Calculus for Electromagnetism 35 : Integration by Parts. If the two-dimensional divergence of a vector field. Chapter 14 - Vector Calculus, Part II (LATEX). 14.4 - Green's Theorem two-dimensional curl. Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: f: f'(x) dx = I(b) -I(a). (c) Use the Divergence Theorem to prove the following integration by parts formula for a closed and bounded region W with boundary S, and f,g : R3 → R . Support us and buy the Calculus workbook with all the packets in one nice spiral bound book. 6.11 Integrating Using Integration by Parts. The integral theorems are identities that typically relate one kind of integral to another (such as a volume integral to an integral over the .

Divergence theorem integration by partsIntegration Formulas for Vectors and Tensors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
